It’s a good time to start new habits – or refresh old ones. Running reports regularly will help you make better business decisions.
Whether or not you made New Year’s resolutions, you probably look at January as a fresh start in personal and professional matters. Unfortunately, we can’t help you join a gym or organize your closets or meet your monthly sales goals.
What we can do, though, is encourage you to start a new habit that may actually leave you more time for those activities and even improve your company’s financial bottom line. We’re talking about committing to using the reporting tools QuickBooks offers.
You can’t possibly know how your business is doing unless you take advantage of this critical feature. It’s the payoff for all the hard work you do keeping up with your daily accounting workflow. Here are five things you should try.
Visit QuickBooks’ Report Center:
As you know. QuickBooks devotes an entire menu to reports, dividing them into types (Sales, Purchases, Inventory, etc.). When you hover your mouse over one of these categories after opening the Reports menu, you’ll see a list of all related reports.
Click on Report Center, though, and you’ll see a kind of home page for reports. They’re categorized by type, just like in the main Reports menu, but there’s much more you can do here.
Click on a report name in the Report Center and you’ll have numerous options.
When you click on the graphic representing a report, you’ll first be able to change the date range by clicking on the down arrow. Then you can Run the report, see a brief explanation by clicking Info, click on Fave to add it to your list of Favorites, or open Help. The tabs at the top of the screen allow you to toggle between these Standard views, reports you’ve Memorized, Favorites, Recent, and Contributed (report templates created by individuals outside of Intuit).
If you know exactly what reports you want to run it’s probably easier to just use the Reports menu, but the Report Center is a great place to learn about and organize your content.
Customize Your Reports:
You’re probably used to changing the date range on your reports, but have you ever explored any of QuickBooks’ other customization tools? You can use them on any report. Click the Customize Report button in the upper left. Click on the Display tab, and you can change the report’s columns by checking or unchecking entries in the list. Filters are more complex, and you may need our help setting up very specific, multi-filter reports. They offer a way to pare down your report to contain just the data you want. You could, for example, prepare a report that only includes one or more Transaction Types or customers who live in a specified state.
Memorize Your Reports:
Once you’ve changed columns and filters in a report you’ll run frequently, you can save those settings so you don’t have to go through all of that again. Open any report and click the Memorize button in the upper toolbar. The window that opens will ask if you want to save that customized report to a Memorized Report Group, which you can do by clicking the box and opening the list of groups. Either way, you can find your report by opening the Reports menu and selecting Memorized Reports.
If you want to create a new Memorized Report Group, open the Reports menu and click Memorized Reports | Memorized Report List. Open the Memorized Report drop-down menu and select New Group.
Schedule Your Reports:
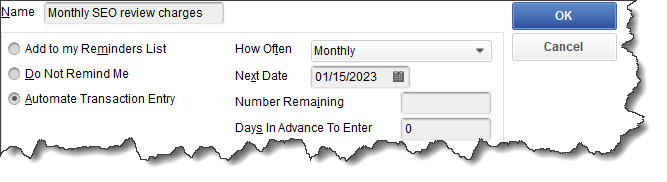
The best way to get your report habit started is by creating a schedule of reports you need to see regularly. You can do this by setting up Reminders (Company | Reminders). Click the gear icon in the upper right corner to specify your Preferences and the + (plus) sign to add a reminder. QuickBooks 2017 and later versions offer a scheduling tool that allows you to share reports with others, but please don’t try this on your own. It’s a complicated procedure with many rules.
You’ve probably noticed that there is a report category called Accountant & Taxes. Some of these should be created monthly or quarterly, but you’ll need our help analyzing them as well.
In the coming year, we strongly encourage you to expand your skills at generating reports. You can’t make realistic, effective plans for the future of your company without knowing its current financial state and its history. So start the year off right in 2020, and let us know how we can help.